Azulfidine : Uses, Side effects, and Interactions

- Azulfidine
- 16 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Azulfidine?
Azulfidine is one of the brand names of the drug sulfasalazine. Other names for Azulfidine may include Salazopyrin and sulfazine. Azulfidine belongs to the drug category of anti-inflammatory drugs. Its usage for ulcerative colitis and both adult and pediatric rheumatoid arthritis was approved by the FDA in the year 2000 1Overview| Researched based study from Fda.gov . It can also be used to treat a few other diseases. This article discusses Azulfidine, dosage, administration, side effects, health benefits, drug interactions, and precautions.
Key Facts
Key facts of Azulfidin
- Azulfidine class – amino salicylates
- It is also categorized as a DMARD, or disease-modifying antirheumatic medication.2Key facts| Researched based study from Guidetopharmacology.com
- Chemical formula – C18H14N4O5S 3Facts| Researched based study from Fda.gov
- This drug is a combination of 5-aminosalicylic acid and sulfa pyridine.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) listed sulfasalazine as one of the essential drugs. 4Facts| Researched based study from Who.int
- It comes in immediate-release and delayed-release forms as oral tablets containing 500 mg of Azulfidine.
- The liver and the intestines’ bacteria liver and the bacteria in the intestines break down this medication in the small intestine.3Facts| Researched based study from Fda.gov
- It is primarily eliminated from the body through urine and feces.3Facts| Researched based study from Fda.gov
How does it work?
We are still unclear about how it works in the body. However, it is thought to have the following effect –
- Anti-inflammatory effect – the drug works by preventing the body from making the chemicals that cause swelling and redness.5Mechanism| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Suppression of immunity – It also can diminish the number of white cells in the blood, limiting the body’s ability to fight infections.6Mechanism| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Uses
Azulfidine uses
The FDA indicates Azulfidine tablets for:
- Treating ulcerative colitis.
- Treating Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Treating Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
It also has off-label uses to:
- Treat ankylosing spondylitis.
- Manage Psoriatic arthritis.
- Treat mild to moderate Crohn’s disease.
Treating ulcerative colitis
- The condition ulcerative colitis, which results in swelling and ulcers in the lining of the large intestine and the rectum, is treated with the FDA-approved medicine Azulfidine.7Uses| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Treating Rheumatoid arthritis
- Adults with rheumatoid arthritis who have not responded well to previous treatments or could not tolerate them are treated with sulfasalazine delayed-release in the form of Azulfidine EN-tabs.5Uses| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
Treating Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (PJIA)
- Children with PJIA who have not responded to previous medications, are treated with Enteric coated Azulfidine tablets.5Uses| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
Treats ankylosing spondylitis
- Sulfasalazine is used for ankylosing spondylitis but only in specific circumstances, such as when no other effective treatments remain owing to toxicity, contraindications, expense, etc.7Uses| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Treats psoriatic arthritis
- Psoriasis is a condition with long-term inflammation of the skin and joints and may be effectively treated with sulfasalazine.8Uses| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Treats mild to moderate Crohn’s disease
- According to the updated guidelines for treating Crohn’s disease, sulfasalazine is beneficial in treating mild to moderately active Crohn’s disease symptoms.9Uses| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Dosage
Dosage & Administration of Azulfidin
The following are possible dosages
For Ulcerative colitis
- Initial dose – 3 to 4 g split into not more than equal eight-hour periods every day.
- Maintenance dose – 2 g divided into no more than equal eight-hour doses per day.
For rheumatoid arthritis
- 1 gram in two divided doses or 500 mg once a day.
- Up to a maximum of 3 g in divided dosages per day.
- 500 mg in split dosages or upwards to 2 to 3 g each day.
For Crohn’s disease
- Up to 16 weeks, take 3 to 6 g every day in split doses.
Psoriatic arthritis
- 500 mg at first, once per day, increasing to two to three grams.
For juvenile idiopathic arthritis – 6 to 16 years
- 2 split dosages of 30 to 50 mg per kg each day, up to a daily limit of 2 grams a day.7Dosage| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
How to take the drug Azulfidine?
- It is preferable to take Azulfidine tablets after meals.10Dosage| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Azulfidine-EN is an enteric-coated tablet used for delayed release; it must be eaten whole without chewing.
- It is advisable to take this medication regularly throughout the day and night without leaving a gap of more than 8 hours in-between.
- People should continue taking this medicine for the entire duration of their therapy even if they start feeling better and should never skip a dose.
Side effects
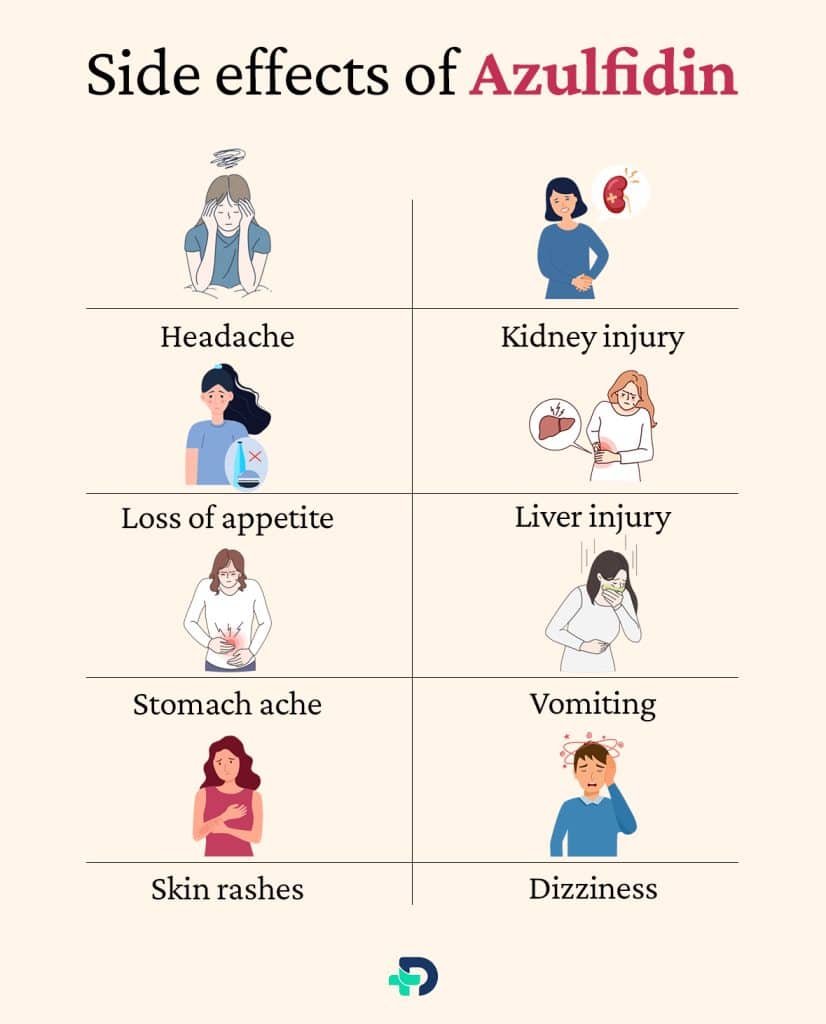
Side effects of Azulfidin
The most common side effects of Azulfidine may include the following
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Stomach ache
- Skin rashes
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dizziness
Less common side effects that may need medical attention
- Reversible male infertility
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
- Bleeding
- Bruising
Allergic reactions
- Itching
- Skin rash
- Hives
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
Kidney injury
- Urine output reduction
- Swollen hands and feet
Liver injury
- Right upper belly pain 11Side effects| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Light-colored stool
- Dark or brown urine
- Yellowing of skin or eyes
- Loss of appetite
- Unusual weakness
Who should not take Azulfidine?
- Those who are allergic to sulfasalazine.
- Those who are allergic to sulfonamides or salicylates.
- Individuals who suffer from porphyria.
- People who have a urinary blockage
- Individuals who have intestinal blockage
Precautions
Precautions to be take while using Azulfidin
- Before using this medication, patients with known allergies to salicylate, sulfasalazine, or sulphapyridine should tell their doctor.
- Caution should be taken when giving Azulfidine pills to people with severe asthma or allergies.
- Enough water should be consumed to avoid kidney injury or the production of stones.
- Patients who lack glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase should be continuously monitored for symptoms of hemolytic anemia.
- If a patient has a blood disorder in their family, kidney or liver illness, or kidney stones, they should inform the doctor.
- If hypersensitive reactions happen, the medication should be stopped right away.
- Before using this medication, pregnant women who plan to get pregnant should tell their doctor.
- Since the medicine may be transferred to the infant through breast milk, breastfeeding moms should let their doctors know.
- People need to be aware that Azulfidine can temporarily lower male fertility, which reverses after the medication is stopped.
- Limit the time spent in the sun and wear sunscreen, sunglasses, and protective clothes while taking sulfasalazine, as it may make the skin photosensitive.
- Some people’s urine may change to orange. Do not worry; it is harmful and fades away as the medicine stops.
- This medicine may also affect some lab test results, including liver function tests and urine tests, leading to possible abnormal test results. Assure that all of your medical professionals, including the lab staff, knows that you take this drug.
Interactions
Azulfidin Interactions
Azulfidine may interact with the following drugs
- Folic acid – may have a reduced absorption when used with Azulfidine. 12Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Digoxin – absorption has been observed to be decreased by sulfasalazine due to changes in the gut wall’s characteristics.13Interactions| Researched based study from Pdr.net
- Mesalamine – To prevent overdosing, sulfasalazine shouldn’t be given with mesalamine because it will be converted to it in the intestine.13Interactions| Researched based study from Pdr.net
- Anti-diabetic drugs – When combined with asulfidine, anti-diabetic medications like metformin may have a more significant blood glucose-lowering impact and a higher risk of hypoglycemia.13Interactions| Researched based study from Pdr.net
- Warfarin – when co-administered with sulfonamides, careful monitoring of the INR should be done since this may increase warfarin exposure and raise the risk of bleeding.8Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Isoniazid – a medication used to treat tuberculosis, increases the risk of liver damage when used with sulfasalazine 14Interactions| Researched based study from Rheumatology.org
Before taking Azulfidine, it is recommended that people discuss all the medications they are currently taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines, herbal drugs, and supplements, as the above list of drug interactions does not cover all the medications known to interact with Azulfidine.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
U.S Food and Drug Administration
Azulfidine | Overview
-
BPS Guide to Pharmacology
Sulfasalazine | Facts
-
U.S Food and Drug Administration
Azulfidine®-sulfasalazine tablets, USP | Facts
-
World Health Organization
World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines | Facts
-
Medline Plus
Sulfasalazine | Mechanism
-
National Library of Medicine
Sulfasalazine prevents T-helper 1 immune response by suppressing interleukin-12 production in macrophages | Mechanism
-
National Library of Medicine
Sulfasalazine | Uses
-
National Library of Medicine
Sulfasalazine therapy for psoriatic arthritis: a double blind, placebo controlled trial | Uses
-
National Library of Medicine
Highlights From the New ACG Guideline on Crohn’s Disease Management | Uses
-
Mayo Clinic
Sulfasalazine (Oral Route) | Dosage
-
Cleveland Clinic
Sulfasalazine Tablets | Side effects
-
National Library of Medicine
Does sulphasalazine cause folate deficiency in rheumatoid arthritis? | Interactions
-
Prescribers' Digital Reference
Sulfasalazine - Drug Summary | Interactions
-
American College of Rheumatology
Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) | Interactions