Lotus root: Nutrition, Health Benefits, and Culinary Tips

- Lotus Root
- 30 Aug 2023
Introduction
What is Lotus root?
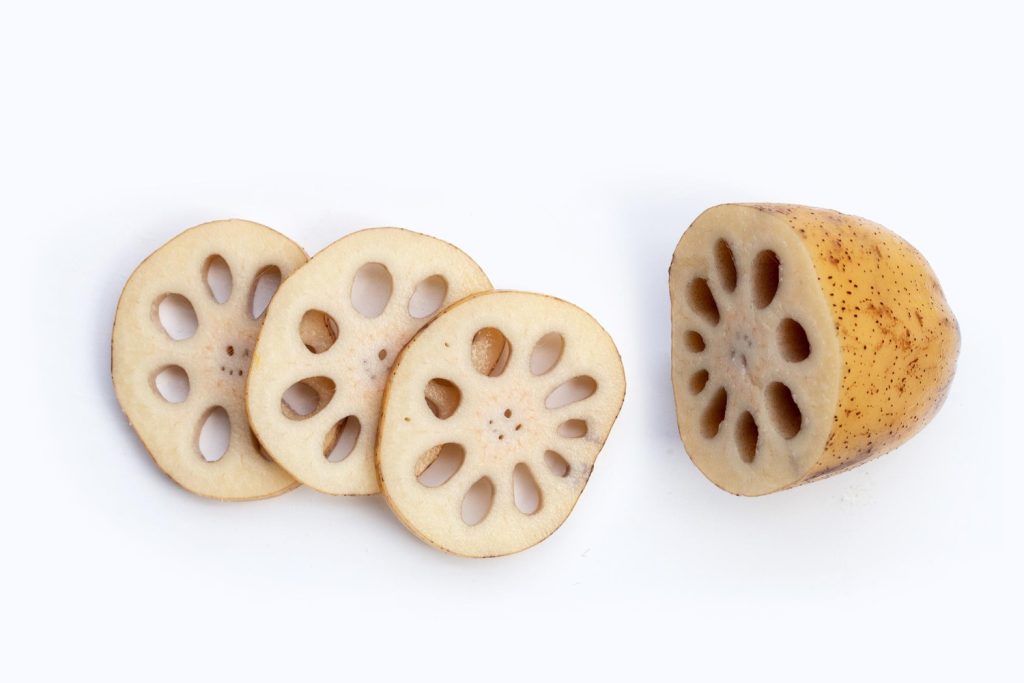
Lotus root is the eatable elongated stalk of the aquatic lotus plant (Nelumbo nucifera) from the Nelumbonaceae family. The lotus root is cylinder-shaped with oval holes to get oxygen and to keep it floating in the water. The interior portion of the root has white crunchy flesh, while the outside is brownish-yellow with a smooth texture. The lotus root has a sweet, nutty aroma, and when sliced, it looks like a wafer making it a popular garnish in food items for most people around the globe. People can consume lotus root in both cooked and raw form. Lotus root is low in calories and has numerous vitamins and minerals with many health benefits.
In this article, we will explore the nutrition of lotus roots, their health benefits, side effects, risks, and some tips to include in the diet.
Here are some quick facts about lotus root
- Lotus root is indigenous to Australia, Asia, and the Middle East, but it is grown throughout the world
- People used lotus root powder in traditional Chinese medicines. 1Introduction | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health

Nutrition
Lotus root Nutrition
60 grams of cooked lotus roots consist of the following nutrients-
- Calories- 40 Kcal
- Fiber- 1.9gm (gram)
- Protein- 1 gm
- Carbohydrate-9.6 gm
- Sugars- 0.3 gm
- Vitamin B- 0.2 mg (milligram)
- Vitamin C- 16.4 mg 2Nutrition | Researched based study from United States Department of Agriculture
Lotus root has a low glycemic index of 33, much lower than potato, so most people prefer to replace potato with lotus root as the carbohydrate source. The glycemic index quantifies food capable of increasing the blood sugar level.
- Vitamin B helps numerous enzymes perform their duties and helps convert the foodstuff into energy for everyday activities.
- Vitamin C helps the body’s collagen formation and assists in keeping the skin and muscles healthy.
Other vitamins and minerals in Lotus root
- Magnesium
- Calcium
- Potassium
- Choline
- Phosphorus
- Iron
- Vitamin B6
- Copper
- Folate
- Sodium 2Nutrition | Researched based study from United States Department of Agriculture
Bio actives in Lotus root:
Polyphenols
- Polyphenols are natural substances present in vegetables, plants, and lotus roots.
- It has antioxidant (detoxifying) properties and prevents the body from cell destruction.
Flavonoids
- It is a natural compound present in fruits, vegetables, and lotus roots.
- It has anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antiviral, and detoxifying properties.
Triterpenes
- It is a natural substance present in plants and lotus roots.
- It has antimicrobial, antitumor, and detoxifying properties. 3Bioactives | Researched based study from United States Department of Agriculture
Benefits

Health Benefits of Lotus root
Lotus has the following health benefits-
- Reduces the risk of diabetes
- Enhances the skin health
- Enhances the brain health
- Promotes digestion and weight loss
- Promotes the heart health
- Boosts the immune response
- Reduces inflammation
- Reduces oral infections
Reduces the risk of diabetes
- In animal studies, lotus extracts decreased the fasting sugar levels in diabetic rats. 4Benefits | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
- However, research is needed in humans to prove the effects of lotus root on humans
Enhances the skin health
- Nutrients in lotus root viz; vitamin C promotes the collagen formation
- It protects the body from the ultraviolet rays of the sun and prevents skin aging 5Benefits | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Enhances the brain health
- Nutrients in lotus roots improve the thinking capacity and brain functioning preventing Alzheimer’s disease. 6Benefits | Researched based study from Nature
Promotes digestion and weight loss
- Fibers in lotus roots improve the bulk of the stool and regularize the bowel movement.
- It also improves satiety and reduces food intake in later meals, decreasing body mass. 7Benefits | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Promotes the heart health
- Potassium in lotus root decreases the body’s total cholesterol
- It also controls blood pressure and reduces the risk of heart ailments. 8Benefits | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Boosts the immune response
- Nutrients in lotus root protect the body against infections
- It promotes the body’s detoxifying abilities and prevents cell destruction. 9Benefits | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Reduces inflammation
- Nutrients in lotus reduce swelling and pain by preventing inflammation.
- It reduces the chances of persistent diseases such as cancer and heart disease. 10Benefits | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Reduces oral infections
- Some test-tube studies indicated that lotus extract prevents bacterial proliferation associated with gum infections and cavities. 11Benefits | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
However, more studies are warranted in humans to prove the effect of lotus root on oral infections.
Varieties
Varieties of Lotus root
- There are around three hundred varieties of lotus with eatable roots.
- One type, the Jingtang lotus root, is elongated, thin, and quite costly compared to other rhizomes that are short and thick.
- Some varieties of lotus have seven holes when sliced, while others have just nine holes.
- Their tastes are similar; seven-hole root variety has a softer stalk, and people usually prefer to use them in soups.
- The nine-hole variety is tuft and goes well with pickles, salads, and deep fry. 12Varieties | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Dosage
Dosage of Lotus root
- There is inadequate research to determine the standard dose of lotus root.
- The most commonly used amounts of lotus capsules are between one to two grams, while for lotus root powder, it is 15 grams daily.
- However, there is limited information on the safety of lotus products. Hence, always speak with the doctor before taking lotus or lotus roots as a supplement. 13Dosage | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Precautions
Precautions of Lotus root
- Pregnant and nursing women – There is inadequate information on whether lotus and lotus root supplements are safe for pregnant women and nursing mothers. So always consult the health care professional before taking lotus and lotus root in medicinal amounts. 14Precautions | Researched based study from ScienceDirect
Side Effects
Side effects
Lotus root is relatively safe for most people when taken in food quantities. However, as with other fruits and vegetables, consuming lotus root might also trigger allergies in some groups of people.
Some symptoms of lotus allergy are as follows-
- Urticaria
- Skin redness
- Itching
- Mouth and lips swelling
- Lightheadedness
- Trouble breathing 15Side effects| Researched based study from Tandfonline
Risks
Potential Risks
- Although lotus root is safe in food quantities and contains many nutrients, some downsides exist.
- When consumed in medicinal quantities, lotus root powder might decrease blood pressure, so diabetic patients must consult the doctor before taking lotus in therapeutic amounts.
- Avoid eating lotus root in raw form as it might harbor the parasite unfavorable for human health. 16Risks | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Who should avoid consuming Lotus roots?
Lotus root might not be suitable for people with the following health issues-
- Allergic to a lotus or lotus root
- Diabetes
- People before two weeks of planned surgery
- People within two weeks of surgery. 16Risks | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Buying & Storage
Buying and Storage of Lotus root
- One can buy lotus root from food stores, groceries, and supermarkets all year round.
- While selecting lotus roots from the farmers market, buy those that are hard in touch, heavy than their size, smooth, and blemish-free.
- Keep unwashed fresh lotus roots in the refrigerator for around 14 days.
- Keep cut and sliced lotus root in a sealed vessel in the refrigerator and utilize it as early as possible.
- Once cooked, store it in the refrigerator and consume it within 1 to two days.
- One can also keep the fresh lotus root in a dark room at room temperature for around two to three days.
Preparation
Preparation of Lotus root
- Before chopping the lotus root, fragment the rootlet and wash them properly under running water to remove dirt and avoid contamination.
- Then trim the outer edge with a knife, peel the outer skin, and cut it into small slices or cubes to use in different recipes.
- Before cooking, one can dip the cut lotus root in a lemon juice or vinegar bowl to prevent browning. 1Risks | Researched based study from Preparation
Tips
Tips to include Lotus root in diet
- Cut the cooked lotus root into small cubes and add to salads to make it more nutritious.
- Add cooked lotus roots to stews and soups to enhance the taste
- Stir fry the lotus root slices and enjoy it as a snack
- Sauté lotus root with any vegetables of your choice and have it as a side dish
- Lotus root also tastes grand when pickled
Takeaways
Key Takeaways
- Lotus root is a nutritious vegetable with many health benefits
- It has a low glycemic index and calories, making it a healthy option for most people
- It has beneficial plant compounds having antitumor, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties
- People can add lotus root as a healthy addition to their diet.
- However, people with health issues must speak to a doctor before consuming lotus root in medicinal amounts.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Institutes of Health
Introduction | Preparation
-
United States Department of Agriculture
Nutrition
-
National Institutes of Health
Bioactives
-
National Institutes of Health
Benefits/ Diabetes
-
National Institutes of Health
Benefits/ Skin
-
Nature
Benefits/ Brain
-
National Institutes of Health
Benefits/ Weight loss
-
National Institutes of Health
Benefits/ Heart
-
National Institutes of Health
Benefits/ Immune response
-
National Institutes of Health
Benefits/ Inflammation
-
National Institutes of Health
Benefits/ Oral infections
-
National Institutes of Health
Varieties
-
National Institutes of Health
Dosage
-
ScienceDirect
Precautions
-
Tandfonline
Side effects
-
National Institutes of Health
Risks