Furosemide: Uses, Dosage, Side effects and Interactions

- Furosemide
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Furosemide?
Furosemide, known by its brand name Lasix, is a potent diuretic widely used in the medical field. It belongs to the class of loop diuretics, also called water pills, and is primarily prescribed to treat swelling due to fluid retention and high blood pressure. Other medical disorders like heart failure, liver cirrhosis, or kidney illness can also contribute to edema or swelling. Furosemide is available in tablet and injectable forms.
This article explores the mode of action, uses, dosage, administration, side effects, risks, contraindications, precautions, and potential drug interactions associated with furosemide.
Furosemide mechanism of action:
- It prevents the kidneys from reabsorbing ions like chloride, sodium, and water.
- It increases sodium, chloride, calcium, magnesium, and water excretion in the urine.1Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- As a result, it lessens swelling and decreases an individual’s blood pressure.
- Because of the considerable potential increase in urine production, furosemide is a potent remedy for several ailments.
Uses
Uses of Furosemide
Furosemide is indicated in many medical conditions due to its diuretic properties. It is commonly used to manage the following:
- Edema (swelling)
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Renal impairment (kidney failure)
- Hypercalcemia (high blood calcium level)
Edema
- The FDA has approved furosemide for use in treating edema brought on by heart failure, cirrhosis of the liver, and kidney problems in adults and children.2Uses| Researched based study from Fda.gov
- In individuals with congestive heart failure, it helps reduce fluid retention, which reduces swelling and enhances breathing.
Hypertension
- Furosemide is frequently recommended as a supplement to other therapies for treating hypertension.3Uses| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- It aids in lowering blood volume, which reduces blood vessel pressure.
Renal Impairment
- Furosemide enhances urine production and prevents fluid overload in patients with acute or chronic kidney disease.2Uses| Researched based study from Fda.gov
Hypercalcemia
- By increasing calcium excretion through the urine, furosemide can treat high calcium levels in the blood.4Uses| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Dosage
Furosemide Dosage
Furosemide dosage varies depending on the individual’s medical condition and response to treatment.
Furosemide oral tablets are available in the following strengths:
- 20 mg
- 40 mg
- 80 mg
Furosemide oral solution is available as:
- 10 mg/ml
- 8 mg/ml (i.e., 40 mg furosemide/5 ml of solution.) 1Dosage| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Dosage in different conditions:
For edema
- For adults – The usual starting dose is 20-80 mg daily, administered orally or intravenously once a day or in two divided doses.5Dosage| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- For children – The dosage for pediatric patients should be determined based on their weight and medical condition.
For high blood pressure
- Adults – the usual starting dose is 40 milligrams twice a day.
- Children – The dosage for pediatric patients should be determined based on their weight and medical condition.
Following the prescribing physician’s instructions and adhering to the prescribed dosage is important.
Administration: How to take Furosemide?
- Furosemide tablets should be consumed with a glass of water.
- To avoid sleep disruptions brought on by an increase in urine frequency, it is best to take the prescription first thing in the morning.
- Injectable forms should be used in a clinical setting under the guidance of a healthcare expert.6Dosage| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- One should not stop taking furosemide without first talking to their doctor as it may result in the reappearance of all the problems it was taken for.
- Never take too little or too much medication compared to what the doctor has prescribed.
Side effects
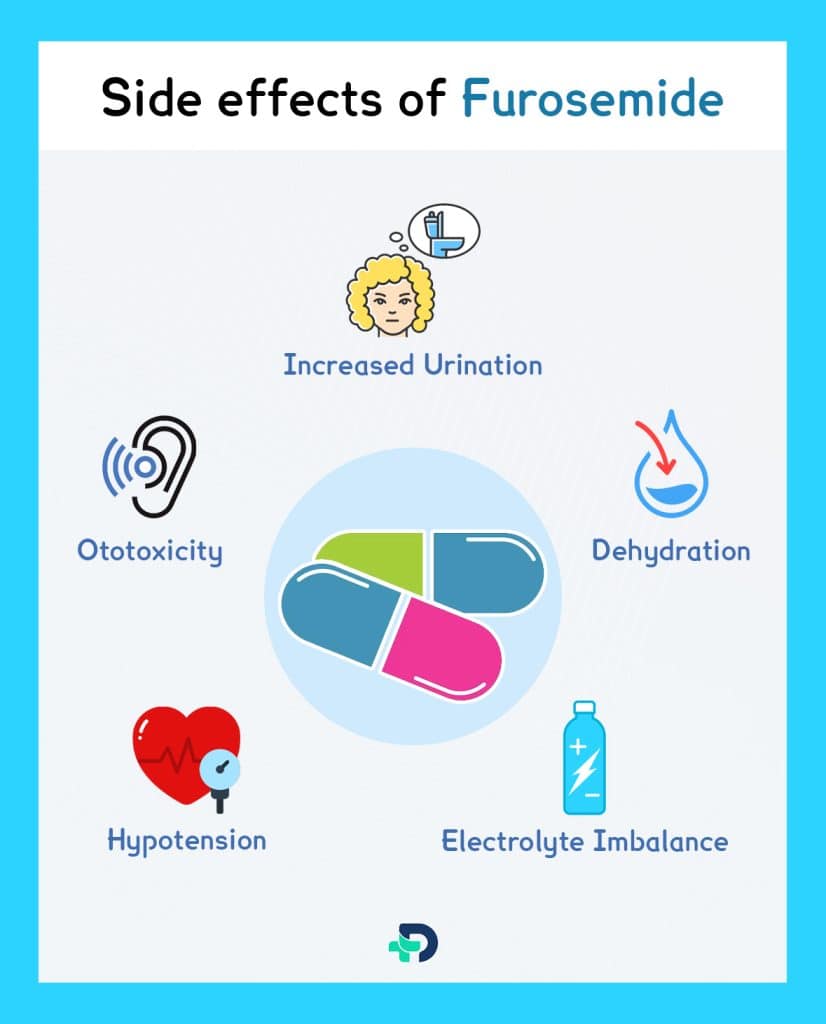
Furosemide Side effects
Like every drug, furosemide has certain undesirable side effects. Furosemide frequently causes side effects like:
- Increased Urination – Furosemide’s diuretic effects can result in an increase in the frequency of urine.
- Electrolyte Imbalance – Furosemide can cause imbalances in the electrolytes, including those in sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium. Regularly monitoring electrolyte levels is necessary, especially in high-dose or long-term treatment.
- Dehydration – Excessive diuresis can result in dehydration, leading to symptoms such as dry mouth, thirst, dizziness, and fatigue7Side effects| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Hypotension – Furosemide can cause low blood pressure, dizziness, or fainting.
- Ototoxicity – Rarely, the drug furosemide may harm the inner ear, resulting in tinnitus or hearing loss.
Additionally, it could cause the following side effects :
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Cramping
- Appetite loss
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Gastric irritation.
- Pain when you eat or drink
- Fever
- Pale skin
- Rapid pulse
- Trouble breathing
- Skin rashes
- Skin itching
- Photosensitivity
- Swollen Face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Ringing in ears , Hearing loss.8Side effects| Researched based study from Dailymed.nlm.nih.gov
- Weakness or Numbness in legs or arms
- A sensation of the room spinning (Vertigo)
- Burning pain or tingling feeling in legs or arms
- Blurred vision
- Headache
- Yellow vision (xanthopsia)
- High blood sugar
- Muscle spasm
- High cholesterol levels
- Low potassium level (hypokalemia)
- Restlessness
When necessary, the dosage should be adjusted and side effects must be reported to the doctor.
According to the FDA, furosemide should be used cautiously because it is a potent diuretic that can cause excess loss of electrolytes and water, leading to dehydration and depletion of electrolytes.2Side effects| Researched based study from Fda.gov
Contraindications
Furosemide contraindications
The following people are recommended not to take furosemide:
- Individuals with known hypersensitivity or allergy to furosemide or sulfonamides.
- People with no urine output.1Contraindication| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Precautions
Precautions
Although furosemide is often safe and well-tolerated, some safety measures should be taken:
- Kidney problems – Furosemide is excreted mainly through the kidneys and should be cautious in patients with poor kidney function, and dosage changes may be required.
- Liver disease – Patients with liver conditions such as liver cirrhosis should use furosemide cautiously because it can further damage liver function.
- Diabetes – Blood sugar levels could be increased with furosemide. While using this drug, diabetic individuals should closely monitor their blood glucose levels.
- Electrolyte imbalance – The following signs or symptoms of fluid or electrolyte imbalance, such as low levels of sodium, chloride, potassium, magnesium, or calcium in the blood, should be kept an eye out in all patients on furosemide therapy.8Precaution| Researched based study from Dailymed.nlm.nih.gov
- Pregnancy – Because furosemide may cross into the womb and potentially harm the developing fetus, it should not be used during pregnancy.
- Breastfeeding – Furosemide may enter the mother’s milk and pass it on to the child. Additionally, it might prevent lactation.8Precaution| Researched based study from Dailymed.nlm.nih.gov
- Older adults – People aged 65 and up should have their serum sodium levels routinely checked at the start of treatment or throughout dose adjustments.1Precaution| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Alcohol – The adverse effects of furosemide, like low blood pressure, lightheadedness, or dizziness, can get worse if you consume alcoholic beverages while taking the medication.1Precaution| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Interactions
Interactions of Furosemide
Various drugs and furosemide may interact, affecting the efficacy or posing a greater risk of adverse consequences. Including over-the-counter medications and dietary supplements, it is critical to let the healthcare professional know about all current medications.
Among the most frequent medication interactions are:
- Aminoglycoside antibiotics – When used with furosemide, aminoglycoside antibiotics may have a more significant potential for ototoxicity, especially in patients with kidney issues. 9Interactions| Researched based study from Fda.gov
- Lithium – Lithium levels may rise and become potentially hazardous due to furosemide’s ability to inhibit the excretion of lithium.9Interactions| Researched based study from Fda.gov
- Sucralfate – furosemide tablets and Sucralfate should not be taken at the same time since it may result in less sodium being excreted and less furosemide’s ability to control blood pressure.8Interactions| Researched based study from Dailymed.nlm.nih.gov
Bottom Line
The Bottom Line
Strong loop diuretic furosemide has proven to be an effective treatment for several illnesses. However, adhering to the recommended dosage is crucial, comprehend potential side effects and being knowledgeable about the dangers, safety measures, and drug interactions related to furosemide. Under the supervision of their healthcare professional, individuals can use this drug securely and profitably as a result.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Furosemide | Overview
-
FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION
FUROSEMIDE TABLETS, USP | Uses
-
Medline plus
Furosemide | Uses
-
National Library of Medicine
Effects of furosemide on renal calcium handling | Uses
-
Mayo Clinic
Drugs and Supplements Furosemide (Oral Route) | Dosage
-
Medline plus
Furosemide Injection | Dosage
-
Cleveland Clinic
Furosemide Injection | Side effects
-
DailyMed
FUROSEMIDE- furosemide tablet | Side effects
-
FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION
LASIX®(furosemide) | Interactions